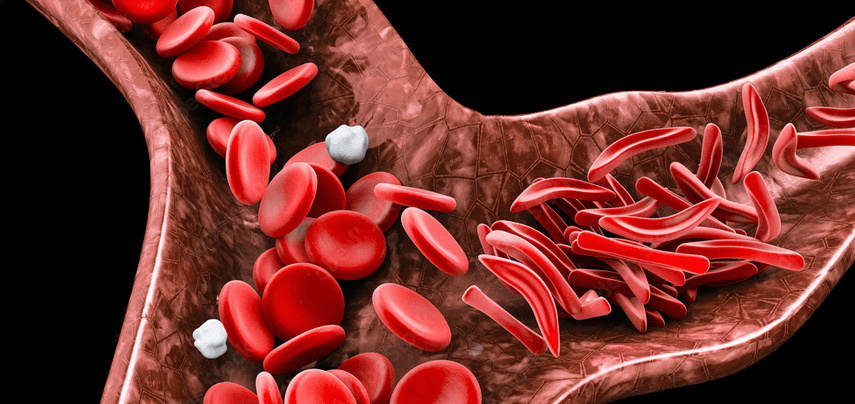
The symptoms of sickle cell anemia include swelling of the hands and feet, delayed growth or puberty, vision problems and frequent infections.
Table of contents
Sickle cell disease (SCD) This is an umbrella term for a group of inherited (genetic) blood disorders affecting hemoglobin, the protein in red blood cells that carries oxygen throughout the body. This condition causes the production of abnormal hemoglobin, leading to red blood cells becoming stiff and sickle-shaped, unlike the normal, flexible, disc-shaped cells.
This is the most common and severe type of SCD. In sickle cell anemia, individuals inherit two copies of the sickle cell gene (HbSS), one from each parent. This results in the body producing mostly sickle-shaped red blood cells, which can block blood flow and cause various health problems
Other Forms of SCD
While sickle cell anemia is the most severe, other types of SCD exist, including those where individuals inherit one sickle cell gene and another gene for a different type of abnormal hemoglobin (like hemoglobin C or beta thalassemia). These forms can also cause symptoms, but severity can vary
Genetic Nature:
SCD is inherited and most commonly affects people of African, Mediterranean, Middle Eastern, and Indian ancestry.
Both parents must carry the sickle cell trait for a child to have the disease
Symptoms and Complications:
Common symptoms include severe pain episodes, fatigue, and anemia.
Complications can include stroke, acute chest syndrome, organ damage, increased risk of infections, and premature death.
Diagnosis and Treatment:
Diagnosis is typically confirmed through a blood test.
Treatment may focus on managing symptoms and preventing complications, including pain management, blood transfusions, and prescribed medications such as hydroxyurea; or on curative therapies such as cell therapy (Bone Marrow and Stem Cell Transplantation) and gene therapy (crispr- Casgevy therapy or ex vivo- Lyfgenia therapy)
Living with SCD:
Regular medical care and healthy lifestyle choices are crucial.
Patients should avoid triggers such as extreme temperatures and dehydration.
Raising awareness about sickle cell disease is essential for early diagnosis and treatment. Support from healthcare providers, communities, and organizations can significantly improve the quality of life for those affected by SCD.
Conclusion
Understanding and managing sickle cell disease is crucial for improving the quality of life for those affected. Awareness of its genetic nature, symptoms, and complications can lead to early diagnosis and effective treatment. Regular medical care and support from healthcare providers and communities play vital roles in managing the condition. By staying informed and proactive, individuals and families can better navigate the challenges of sickle cell disease, leading to healthier, more fulfilling lives.
Articles